leucocytosis specialist doctor in Indore
What is Leucocytosis?
Causes of Leucocytosis
Leucocytosis can arise from several factors. While some are harmless and temporary, others may require immediate medical attention:
Infections
Bacterial, viral, fungal, or parasitic infections are the most common triggers.
Inflammation
Chronic inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis or inflammatory bowel disease often lead to high WBC counts.
Stress
Physical or emotional stress, including injuries, surgeries, or anxiety, may temporarily elevate WBC levels.
Medications
Certain drugs, such as corticosteroids, can stimulate the production of white blood cells.
Bone Marrow Disorders
Conditions like leukemia, lymphoma, or myeloproliferative disorders cause an overproduction of WBCs.
Chronic Illnesses
Diseases like sickle cell anemia or autoimmune disorders can lead to persistent leucocytosis.
Smoking
Smoking causes chronic irritation in the lungs, which may result in an increased WBC count.
How Common Is Leucocytosis?
Leucocytosis, a condition where the white blood cell count is higher than normal, is relatively common and can occur in people of all ages. It often happens temporarily during infections, stress, or inflammation, but sometimes it may signal more serious issues like blood disorders. The exact frequency depends on the underlying cause and health status of a person. Since high white blood cell counts can have many reasons, proper diagnosis is important. If your blood tests show elevated WBC levels, it’s best to consult a leucocytosis specialist doctor in Indore. Dr. Akshay Lahoti offers expert evaluation and advanced treatment to identify the root cause and guide you toward recovery with a clear, patient-friendly approach.
Symptoms of Leucocytosis
Leucocytosis does not always present with symptoms, but when it does, the signs often depend on the underlying cause. Common symptoms include:
- Fever and chills
- Fatigue or persistent weakness
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Night sweats
- Sudden weight loss
- Infections that are slow to heal
- Swelling or redness in parts of the body
If these symptoms occur frequently, consulting a hematologist doctor in Indore like Dr. Akshay Lahoti is highly recommended.
Complications of Leucocytosis
If left untreated, leucocytosis can lead to significant complications, such as:
Tissue Damage
High levels of WBCs can cause inflammation and damage to tissues.
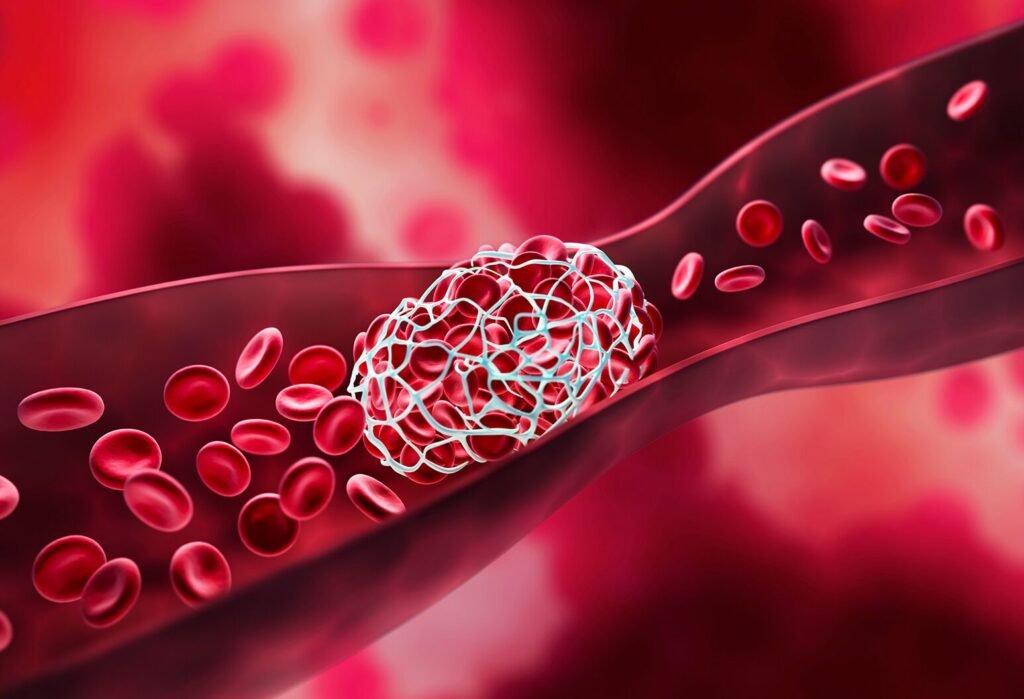
Blood Clots
Thickened blood due to elevated WBC counts increases the risk of clot formation, strokes, or heart attacks.

Weakened Immunity
In cases of leukemia, the abnormal WBCs are often ineffective in fighting infections.
Treatment for Leucocytosis
The treatment for leucocytosis depends on its cause. Common approaches include:
- Antibiotics or Antivirals:
Infections are treated with appropriate medications to lower WBC levels. - Anti-Inflammatory Drugs:
These are used for chronic inflammatory conditions like arthritis. - Chemotherapy and Radiation:
In cases of leukemia or lymphoma, chemotherapy, radiation, or Bone Marrow Transplant may be required. - Stress Management:
Lifestyle changes, including better stress management and relaxation techniques, can help stabilize WBC levels. - Medication Adjustment:
If drugs are contributing to leucocytosis, their dosage may be adjusted or discontinued.
Dr. Lahoti, an experienced blood cancer doctor in Indore, provides personalized treatment plans tailored to each patient’s condition.
Effects and Side Effects of Treatment
While treatments for leucocytosis are generally effective, they can cause side effects:
- Antibiotics: May lead to stomach upset or allergic reactions.
- Chemotherapy: Often causes fatigue, nausea, and hair loss.
- Bone Marrow Transplant: While highly effective, it carries risks such as infections or immune system complications.
With Dr. Akshay Lahoti’s guidance, patients can manage these side effects and recover effectively.
Prevention of Leucocytosis
Although not all cases of leucocytosis can be prevented, certain measures can lower the risk:
- Maintain Hygiene:Regular handwashing and vaccinations reduce the risk of infections.
- Quit Smoking:This lowers the risk of chronic inflammation and lung-related issues.
- Manage Stress:Stress-relieving activities like yoga or meditation can improve overall health.
- Follow a Healthy Diet:A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean protein supports the immune system.
- Regular Check-Ups:Periodic health screenings help detect early signs of blood disorders like anemia, lymphoma, or sickle cell disease.
Frequently Asked Questions
Leucocytosis is a condition with elevated white blood cells, often from infections or serious illnesses. For accurate diagnosis and care, consult the best hematologist in Indore to identify the cause and begin proper treatment.
Leucocytosis is diagnosed through a Complete Blood Count (CBC). Additional tests like a peripheral blood smear, bone marrow biopsy, or infection screening might be needed. A trusted blood cancer doctor in Indore, such as Dr. Akshay Lahoti at Medicare Hospital, can provide an accurate diagnosis.
While leucocytosis itself isn’t always harmful, it can indicate serious underlying conditions like bone marrow disordersor lymphoma. Untreated cases can lead to complications like blood clots or weakened immunity. Visit Medicare Hospital to address your concerns promptly.
Treatment depends on the cause. Options include antibiotics for infections, anti-inflammatory medications for chronic conditions, and specialized procedures like Bone Marrow Transplant for blood cancers. Dr. Akshay Lahoti, a renowned hematologist doctor in Indore, provides personalized treatment plans at Medicare Hospital.
Prevention involves maintaining good hygiene, managing stress, eating a balanced diet, and avoiding smoking. Regular health check-ups with a hematologist doctor at Palasia can help detect and treat conditions early.
Side effects of leucocytosis treatment in Indore may include fatigue, nausea, mild fever, or infection risk, depending on the cause and therapy. Expert care ensures side effects are managed while addressing the underlying condition effectively.
