Polycythemia Vera: Key Information on Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment from Dr. Akshay Lahoti in Indore

What is Polycythemia Vera?
Polycythemia Vera (PV) is a rare blood disorder in which the body makes too many red blood cells. This increases the thickness (viscosity) of the blood, making it harder for it to flow properly. This can lead to complications, including blood clots, which could be dangerous for the heart, brain, and other organs. Hematologist Dr. Akshay Lahoti, with over 7 years of experience in clinical hematology, has successfully treated many patients suffering from this condition at Medicare Hospital in Indore. In this article, we will discuss the causes, symptoms, complications, diagnosis, and treatment options for Polycythemia Vera.
Complications of Polycythemia Vera
If left untreated, Polycythemia Vera can cause severe complications, including:
Blood Clots
Thickened blood increases the risk of clots forming in the blood vessels, which can lead to strokes, heart attacks, or deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
Enlarged Spleen and Liver
The overproduction of blood cells can lead to an enlarged spleen and liver, causing discomfort and pain.
Bleeding
Despite having too many red blood cells, some patients with PV may experience abnormal bleeding because the increased cell count affects platelet function.
Myelofibrosis
Over time, Polycythemia Vera can cause the bone marrow to become scarred, a condition known as myelofibrosis, which can lead to severe anemia.
How Common Is Polycythemia Vera?
Polycythemia Vera is a rare condition. It is estimated that around 1 to 2 people in every 100,000 develop this disorder. It can occur in both men and women but is most commonly diagnosed in people over the age of 60. In India, the number of reported cases is relatively low, but it still presents a significant health challenge. Since it is a blood cancer disorder, many people seek the guidance of experienced hematologists, like Dr. Akshay Lahoti in Indore, to manage and treat the disease.
What Causes Polycythemia Vera?
Polycythemia Vera is caused by a mutation in the bone marrow, where blood cells are made. This mutation affects a gene called JAK2, leading to an overproduction of red blood cells. The exact cause of this mutation is unknown, but it can develop over time, often without any obvious external trigger. In rare cases, family history may play a role.
Diagnosis of Polycythemia Vera
To diagnose Polycythemia Vera, doctors typically perform a combination of physical exams, blood tests, and bone marrow tests. Key tests include:
Complete Blood Count (CBC)
This test helps determine if you have an increased number of red blood cells.
JAK2 Mutation Test
A blood test that checks for mutations in the JAK2 gene, which are present in most cases of PV.
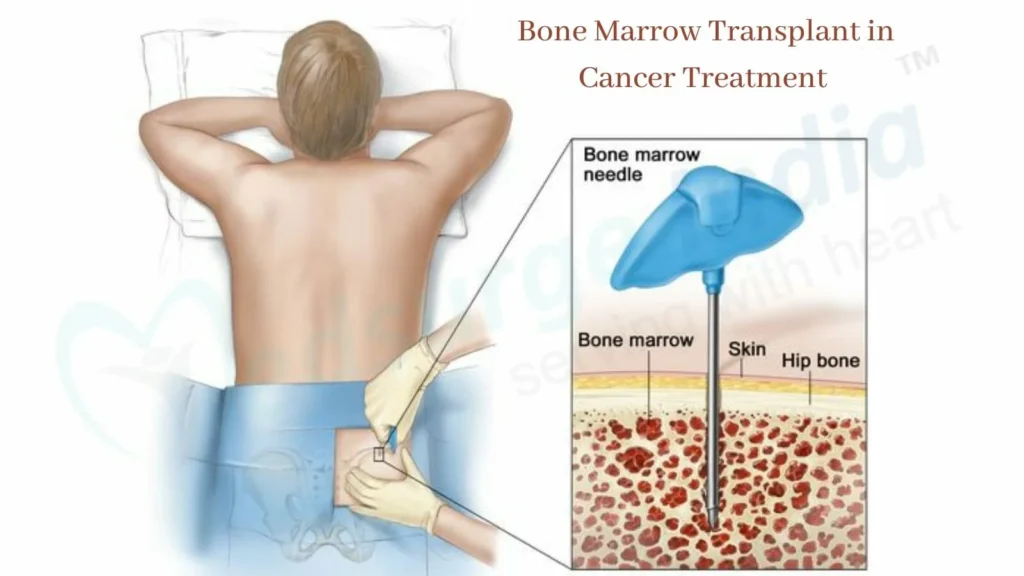
Bone Marrow Biopsy
This procedure involves taking a small sample of bone marrow to check for abnormalities in the cells.
Erythropoietin (EPO) Level
A low level of erythropoietin, a hormone that stimulates red blood cell production, is often seen in PV.
Effects and Side Effects of Treatment
While treatments are generally effective, there are potential side effects. For example, phlebotomy can cause fatigue and low iron levels. Medications like hydroxyurea may cause nausea, vomiting, and other gastrointestinal symptoms. The use of JAK2 inhibitors may also lead to side effects such as infections, bruising, or changes in blood cell counts.
How Many People Have Polycythemia Vera in India?
In India, Polycythemia Vera remains a relatively rare disease, but as awareness grows, more cases are being diagnosed. Due to the advanced diagnostic tools available at hospitals like Medicare Hospital in Indore, many people with PV are now receiving proper treatment and care. While there is no exact number for India, it is believed that the prevalence is low compared to other blood cancers like lymphoma or leukemia.
Frequently Asked Questions
Polycythemia Vera is a rare blood disorder in which the body produces too many red blood cells. This can cause the blood to become thicker, leading to potential complications like blood clots. A hematologist Doctor in Indore, such as Dr. Akshay Lahoti, can help manage this condition effectively.
Polycythemia Vera is relatively rare in India, affecting a small number of people compared to other blood disorders like lymphoma or anemia. However, more cases are being diagnosed with the help of advanced diagnostic tools at hospitals like Medicare Hospital in Indore.
Common symptoms include headaches, dizziness, fatigue, shortness of breath, itchy skin (especially after a warm shower), and an enlarged spleen. If you experience any of these symptoms, consulting a hematologist doctor at Palasia is recommended.
PV is primarily caused by a mutation in the JAK2 gene that leads to an overproduction of red blood cells in the bone marrow. The exact cause of this mutation is unknown, but it often develops over time.
Treatment options include phlebotomy (removing blood to reduce red blood cell count), medications like hydroxyurea, and newer drugs such as JAK2 inhibitors. For severe cases, a Bone Marrow Transplant may be considered. Dr. Akshay Lahoti, a hematologist in Indore, provides customized treatment for PV patients.
? Treatments like phlebotomy and medications can cause side effects such as fatigue, low iron levels, nausea, or bruising. It’s important to work closely with your hematologist doctor at Palasia to minimize these side effects.
