Thrombocytopenia: What It Is and How it is Treated by Dr Akshay Lahoti at Medicare Hospital, Indore
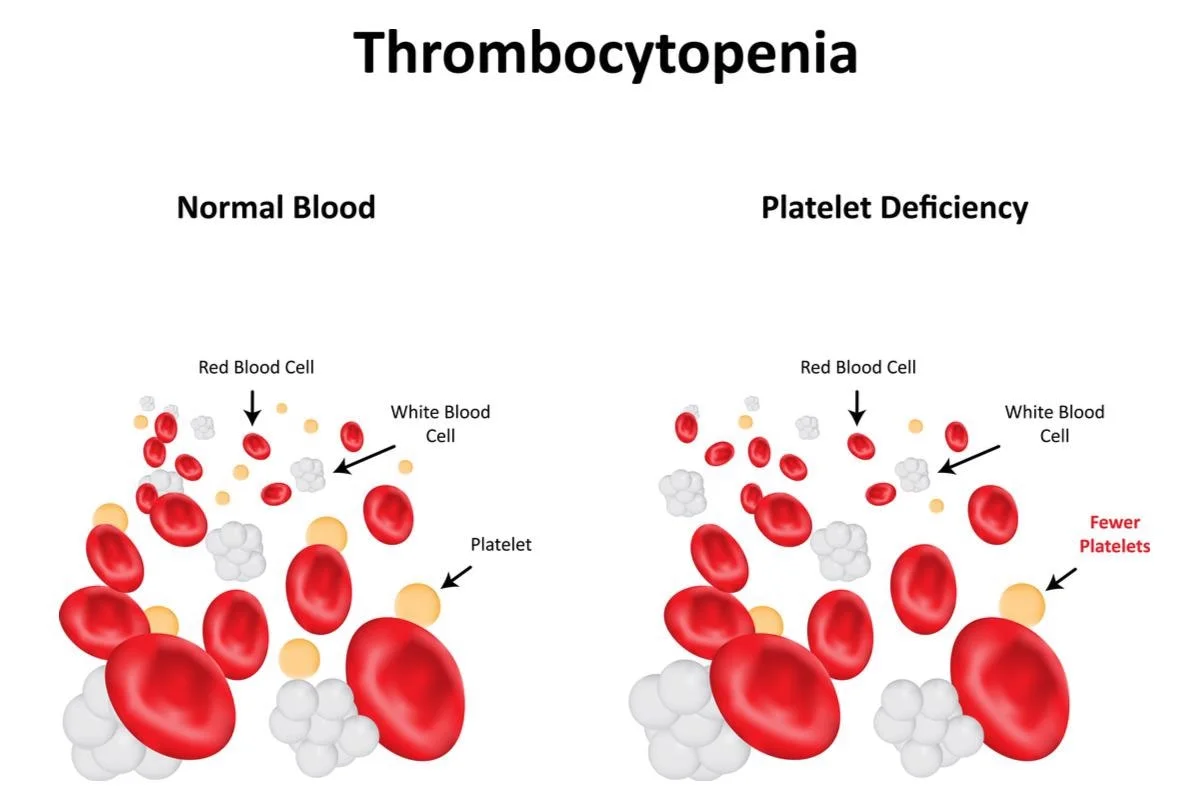
What is Thrombocytopenia ?
Thrombocytopenia is a condition where the body doesn’t have enough platelets, which are tiny cells in your blood that help stop bleeding. Platelets act like mini band-aids, sealing up cuts and injuries to prevent blood from flowing out too much. Without enough of these platelets, even small cuts can cause serious bleeding. Dr. Akshay Lahoti, a hematologist with 7 years of experience, treats patients with thrombocytopenia at Medicare Hospital in Indore.
What Are the Symptoms of Blood Cancer?
Blood cancer can cause several symptoms:
Extreme Fatigue
Low red blood cells can make you feel very tired.
Frequent Infections
Anemia is facilitated by irregular red blood cells.
Weight Loss
Losing weight without trying could be a sign of blood cancer.
Easy Bruising
Low platelet counts can cause bruises or bleeding from small cuts.
Bone Pain
Bone pain can be a symptom of blood malignancy.
Swollen Lymph Nodes
If you have lymphoma, you might notice swollen lymph nodes in your neck, armpits, or groin.
How Common is Thrombocytopenia?
Thrombocytopenia is a common condition. It can affect anyone, from children to adults, and it has many causes. Sometimes, it’s a result of something simple, like a viral infection, while other times it can be linked to more serious health problems like blood cancers. People who have conditions like lymphoma, sickle cell anemia, or those who have had a Bone Marrow Transplant are more likely to develop thrombocytopenia.
Complications of Thrombocytopenia
If thrombocytopenia is not treated, it can lead to dangerous problems. Platelets help your blood clot, and without enough of them, there’s a risk of severe bleeding. This bleeding can happen inside your body (like in your brain) or on the outside. Some people might bruise easily or have long-lasting nosebleeds. For people with blood cancer, the risks can be even higher, which is why getting care from a specialist like Dr. Akshay Lahoti at Medicare Hospital is crucial.
Symptoms and Causes
Symptoms of thrombocytopenia can range from mild to severe. Some common signs include:
- Easy bruising
- Bleeding that’s hard to stop from cuts
- Bleeding gums or frequent nosebleeds
- Small red and purple spots on the skin, called petechiae
- Blood in urine or stool
As for the causes, there are quite a few. Some of the main reasons thrombocytopenia happens include
- Viral infections like dengue or hepatitis
- Autoimmune disorders occur when the body mistakenly assaults its own cells.
- Blood cancers like leukemia or lymphoma
- Certain medications
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Genetic conditions like sickle cell anemia
Treatment for Thrombocytopenia
The treatment for thrombocytopenia depends on its severity and what’s causing it. Sometimes, if the condition is mild, no treatment is needed. However, in more serious cases, doctors may recommend:
Medications
Drugs like steroids can help by stopping the immune system from attacking the platelets.
Blood or Platelet Transfusions
In severe cases, patients may need transfusions to increase the number of platelets in their blood.
Bone Marrow Transplant
This is used in extreme cases, especially for patients with blood cancers like lymphoma. A Bone Marrow Transplant can help the body start making healthy new blood cells again.
Effects and Side Effects
If thrombocytopenia is not treated, it can cause dangerous bleeding. However, treatments also come with possible side effects. For example:
- Steroids can cause side effects like weight gain or mood swings.
- Blood transfusions can sometimes lead to allergic reactions or infections.
- Bone Marrow Transplants have their own risks, including the possibility of infections or other complications, but they can also be life-saving in severe cases.
Prevention: How to Lower the Risk
There are some ways to lower your chances of developing thrombocytopenia, though it can be difficult to completely prevent it.
- Avoid excessive alcohol consumption, as it can lower platelet levels.
- Get vaccinated to prevent viral infections that can affect platelet count, like hepatitis or dengue.
- If you have a family history of blood disorders, get regular check-ups to catch any potential problems early.
If you or someone you know starts showing symptoms of thrombocytopenia, it’s important to see a doctor right away. Getting helps from a specialist like Dr. Akshay Lahoti, a blood cancer doctor in Indore, can make all the difference in managing the condition and preventing serious complications.
Frequently Asked Questions
Thrombocytopenia is a condition where the blood has a low number of platelets. Platelets are important because they help the blood clot and stop bleeding. Without enough platelets, even small cuts or injuries can cause excessive bleeding.
Thrombocytopenia can be caused by various factors, such as viral infections (like dengue or hepatitis), autoimmune diseases, certain medications, blood cancers like leukemia or lymphoma, or genetic conditions like sickle cell anemia.
The common symptoms include easy bruising, frequent nosebleeds, bleeding gums, small red or purple spots on the skin (petechiae), blood in the urine or stool, and excessive bleeding from minor cuts.
Treatment depends on the severity of the condition. Mild cases may not need treatment, while more severe cases may require medications like steroids, blood or platelet transfusions, or even a bone marrow transplant if the condition is related to blood cancer.
Without enough platelets, patients are at risk of excessive bleeding, which can lead to dangerous complications like internal bleeding or bleeding in the brain. If left untreated, it can become life-threatening.
